Dr. John G. Trump, an uncle of former President Donald Trump, was a significant figure in the technological advancements during World War II. Born to German immigrant parents in New York City in 1907, he distinguished himself not on the battlefield, but through his contributions to science and technology, particularly in the development of radar and radiation therapy.
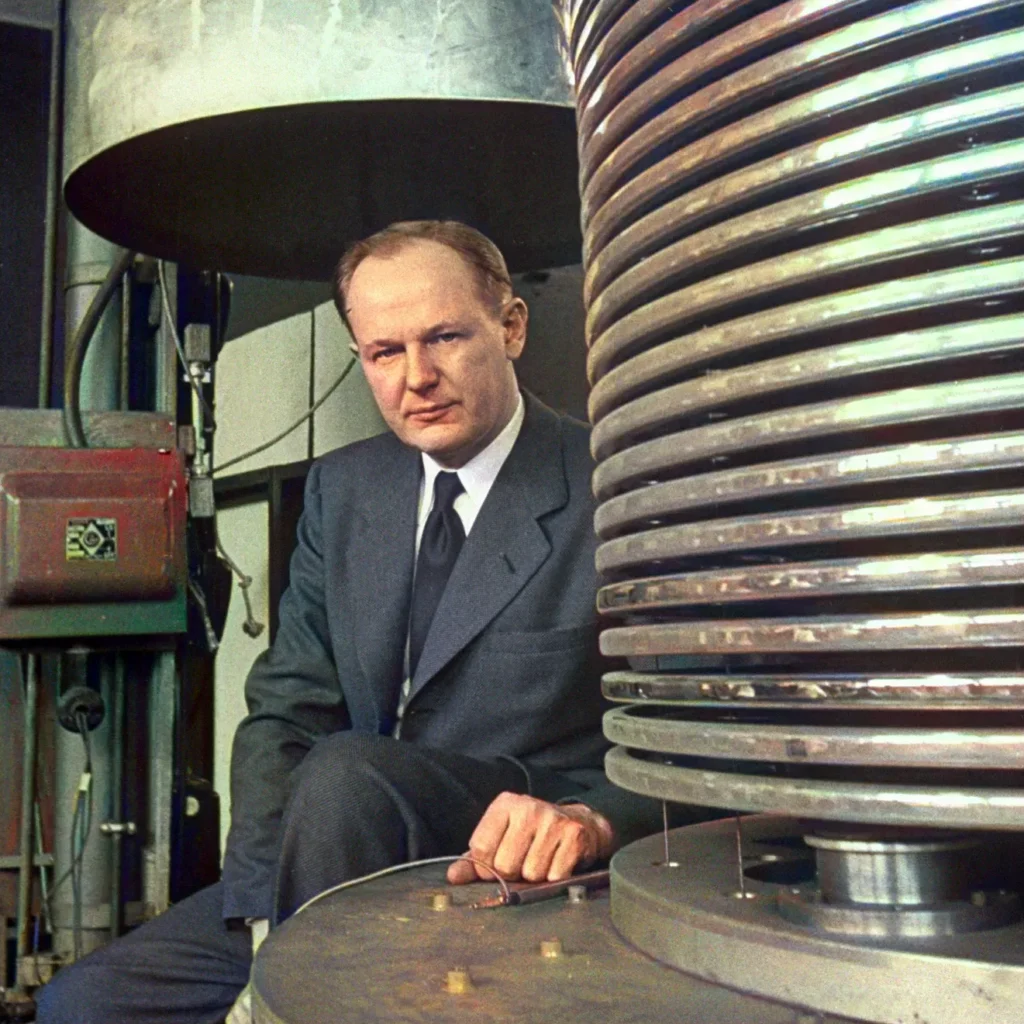
Educated at the Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn and later at Columbia University and MIT, Dr. Trump’s academic and professional career was marked by a deep commitment to electrical engineering and physics. He joined MIT as a professor, a position he maintained until 1973, and was instrumental in wartime research that significantly influenced the Allied war effort.
During the war, Dr. Trump was a key member of the National Defense Research Committee, focusing on radar technology, which was crucial in the air defense strategies employed in battles such as the Battle of Britain. His efforts were recognized by both the British and American governments, earning him prestigious awards, including the King’s Medal for Service in the Cause of Freedom from Britain and the President’s Certificate of Merit from the U.S.
Key Points:
- 🎖️ Honored Scientist: Dr. John G. Trump received significant recognitions, including the King’s Medal for Service and the President’s Certificate of Merit.
- 📡 Radar Technology: His work on radar technology was vital in advancing Allied air defense capabilities, particularly during the Battle of Britain.
- 🏫 Academic Excellence: Dr. Trump’s career at MIT and his educational background highlight his contributions to electrical engineering and physics.
- 🔬 Post-War Contributions: After the war, he continued to innovate, particularly in medical technologies and environmental engineering.
- 🌐 Legacy: Dr. Trump’s scientific achievements not only impacted military technology but also had broad implications for post-war scientific advancements.
Dr. Trump’s legacy is a testament to the crucial role of science and technology in shaping the outcome of World War II and advancing public welfare through innovation in various fields.
